Page 72 - EMCAPP-Journal No. 4
P. 72
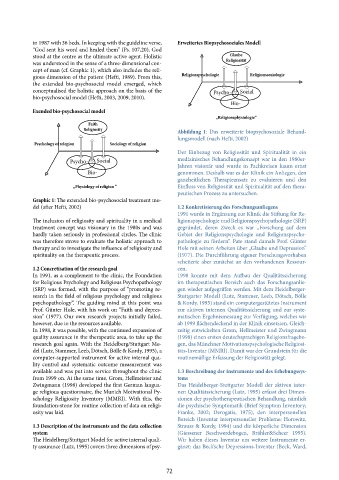
in 1987 with 36 beds. In keeping with the guideline verse, Erweitertes Biopsychosoziales Modell
“God sent his word and healed them” (Ps. 107,20), God
stood at the centre as the ultimate active agent. Holistic Glaube
Religiosität
was understood in the sense of a three-dimensional con-
cept of man (cf. Graphic 1), which also includes the reli-
gious dimension of the patient (Hefti, 1989). From this, Religionspsychologie Religionssoziologie
the extended bio-psychosocial model emerged, which
conceptualised the holistic approach on the basis of the Psycho- Sozial
bio-psychosocial model (Hefti, 2003, 2009, 2010).
Bio-
Exended bio-psychosocial model
„Religionsphysiologie“
Faith
Religiosity
Abbildung 1: Das erweiterte biopsychosoziale Behand-
lungsmodell (nach Hefti, 2002)
Psychology of relegion Sociology of religion
Der Einbezug von Religiosität und Spiritualität in ein
Psycho- Social medizinisches Behandlungskonzept war in den 1980er-
Jahren visionär und wurde in Fachkreisen kaum ernst
Bio- genommen. Deshalb war es der Klinik ein Anliegen, den
ganzheitlichen Therapieansatz zu evaluieren und den
„Physiology of religion “ Einfluss von Religiosität und Spiritualität auf den thera-
peutischen Prozess zu untersuchen.
Graphic 1: The extended bio-psychosocial treatment mo-
del (after Hefti, 2002) 1.2 Konkretisierung des Forschungsanliegens
1991 wurde in Ergänzung zur Klinik die Stiftung für Re-
The inclusion of religiosity and spirituality in a medical ligionspsychologie und Religionspsychopathologie (SRP)
treatment concept was visionary in the 1980s and was gegründet, deren Zweck es war „Forschung auf dem
hardly taken seriously in professional circles. The clinic Gebiet der Religionspsychologie und Religionspsycho-
was therefore strove to evaluate the holistic approach to pathologie zu fördern“. Pate stand damals Prof. Günter
therapy and to investigate the influence of religiosity and Hole mit seinen Arbeiten über „Glaube und Depression“
spirituality on the therapeutic process. (1977). Die Durchführung eigener Forschungsvorhaben
scheiterte aber zunächst an den vorhandenen Ressour-
1.2 Concretisation of the research goal cen.
In 1991, as a complement to the clinic, the Foundation 1998 konnte mit dem Aufbau der Qualitätssicherung
for Religious Psychology and Religious Psychopathology im therapeutischen Bereich auch das Forschungsanlie-
(SRP) was formed, with the purpose of “promoting re- gen wieder aufgegriffen werden. Mit dem Heidelberger-
search in the field of religious psychology and religious Stuttgarter Modell (Lutz, Stammer, Leeb, Dötsch, Bölle
psychopathology”. The guiding mind at this point was & Kordy, 1995) stand ein computergestütztes Instrument
Prof. Günter Hole, with his work on “Faith and depres- zur aktiven internen Qualitätssicherung und zur syste-
sion” (1977). Our own research projects initially failed, matischen Ergebnismessung zur Verfügung, welches wir
however, due to the resources available. ab 1999 flächendeckend in der Klinik einsetzten. Gleich-
In 1998, it was possible, with the continued expansion of zeitig entwickelten Grom, Hellmeister und Zwingmann
quality assurance in the therapeutic area, to take up the (1998) einen ersten deutschsprachigen Religionsfragebo-
research goal again. With the Heidelberg/Stuttgart Mo- gen, das Münchner Motivationspsychologische Religiosi-
del (Lutz, Stammer, Leeb, Dötsch, Bölle & Kordy, 1995), a täts-Inventar (MMRI). Damit war der Grundstein für die
computer-supported instrument for active internal qua- routinemäßige Erfassung der Religiosität gelegt.
lity control and systematic outcome measurement was
available and was put into service throughout the clinic 1.3 Beschreibung der Instrumente und des Erhebungssys-
from 1999 on. At the same time, Grom, Hellmeister and tems
Zwingmann (1998) developed the first German langua- Das Heidelberger-Stuttgarter Modell der aktiven inter-
ge religious questionnaire, the Munich Motivational Py- nen Qualitätssicherung (Lutz, 1995) erfasst drei Dimen-
schology Religiosity Inventory (MMRI). With this, the sionen der psychotherapeutischen Behandlung, nämlich
foundation-stone for routine collection of data on religi- die psychische Symptomatik (Brief Symptom Inventory;
osity was laid. Franke, 2002; Derogatis, 1975), den interpersonellen
Bereich (Inventar interpersoneller Probleme; Horowitz,
1.3 Description of the instruments and the data collection Strauss & Kordy, 1994) und die körperliche Dimension
system (Giessener Beschwerdebogen, Brähler&Scheer 1995).
The Heidelberg/Stuttgart Model for active internal quali- Wir haben dieses Inventar um weitere Instrumente er-
ty assurance (Lutz, 1995) covers three dimensions of psy- gänzt: das Beck’sche Depressions-Inventar (Beck, Ward,
72 72