Page 12 - EMCAPP-Journal No. 4
P. 12
genuine from false forgiveness. However, with the Chris- The explicitly Christian psychological model holds that,
tian Psychology model, it is possible to make a conside- in the course of the journey to forgiveness, one’s view of
rably more precise and refined delineation for counter- sin becomes ever closer to what God reveals as sin; and
feit or false forgiveness, a third distinctive. This is simply accordingly, to some extent a convergence with an objec-
because we can draw from a relatively specific revelation tive view of sin occurs. I maintain that only the Christian
about what sin and wrong are and what forgiveness ul- five-phase model can depict in a precise way the course
timately involves, something secular psychology cannot that this journey takes towards objectivity, and the dif-
do. In all models it is important, if one truly wants to ficulties and limitations that may be encountered. As no-
forgive, to be clear about what is considered to be wrong ted earlier, objectivity, according to the Christian para-
or sin. The corresponding phase in the model by Enright digm, is how God sees things (his perspective), which is
and Reed is named the “Uncovering Phase” whereas ac- (partly) accessible through a process dependent upon his
cording to Shults and Sandage’s model, it is called “Enga- revelation, especially in the Bible but also in prayer and in
ging in Lament” and in Soldan’s model, “Settling up/Fin- every activity of (self)exploration under the guidance of
ding the Truth”. In all three models, the central beginning the Holy Spirit, which includes also natural means, inclu-
point is how the person in question subjectively experi- ding psychotherapy.
ences the wrong done to him or her, and/or subjectively
experiences the wrong he or she has done for which he or
she seeks forgiveness.
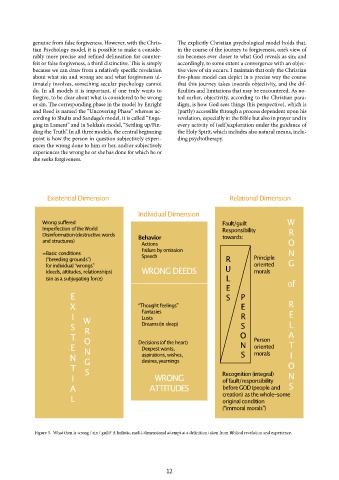
Existential Dimension Relational Dimension
Individual Dimension
Wrong suffered Fault/guilt W
Imperfection oftheWorld Responsibility
Disinformation(destructive words Behavior towards: R
and structures) O
Actions
Failure by omission
=Basic conditions Speech N
(“breeding grounds”) R Principle
forindividual “wrongs” U oriented G
(deeds,attitudes, relationships) WRONGDEEDS morals
(sin asa subjugating force) L of
E
E S P
X “Thought feelings” E R
Fantasies
I W Lusts R E
S R Dreams(in sleep) S L
T O O Person A
E N Decisions(of the heart) N oriented T
Deepest wants,
N G aspirations, wishes, S morals I
desires,yearnings
T S O
I WRONG Recognition(integral) N
of fault/responsibility
A ATTITUDES beforeGOD(people and S
creation) asthe whole-some
L originalcondition
(“immoral morals”)
Figure 3. What then is wrong / sin / guilt? A holistic, multi-dimensional attempt at a definition taken from Biblical revelation and experience.
12 12